Otoplasty for Child: A Parent’s Essential Guide
What is Otoplasty
Definition
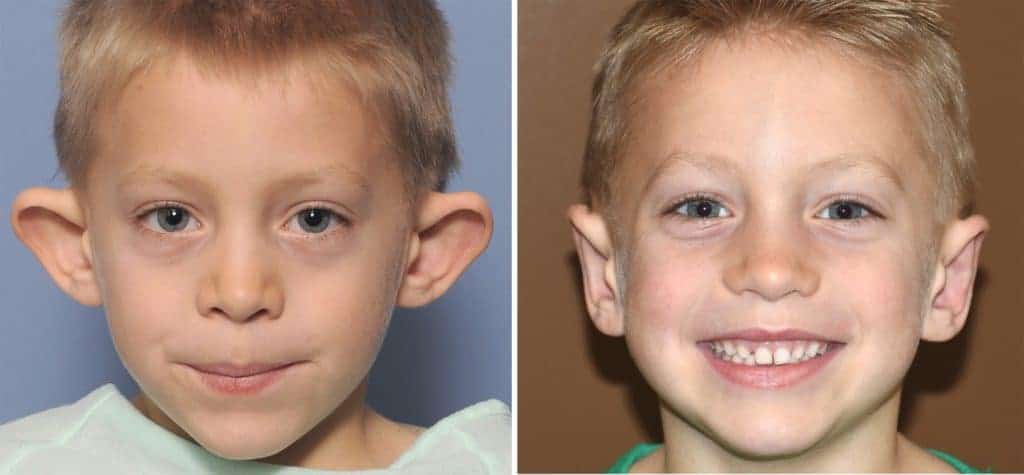
Otoplasty is a surgical procedure. It corrects protruding ears by reshaping the ear cartilage. This surgery is also known as cosmetic otoplasty. The goal is to create a natural ear shape. Surgeons perform it to improve appearance and function.
Typical Age
Children usually undergo otoplasty between ages 5 and 7. At this age, the ears have reached about 90% of their adult size, according to otolaryngology and often considered by parents before opting for otoplasty surgery or using an earband. This maturity reduces the risk of changes post-surgery. Younger children may not be emotionally ready for surgery.
Dual Goals
Otoplasty aims to enhance ear appearance. It also boosts the child’s self-confidence. Children with prominent ears often face teasing. This can affect their emotional well-being. Correcting the shape of large external ears helps them feel better about themselves.
Ear Reshaping
The surgery involves several steps:
- An incision is made behind the ear.
- The surgeon reshapes or removes part of the ear cartilage with an earband and plas.
- The ear is repositioned closer to the head.
- Stitches are used to close the incision.
This process creates a more natural ear contour.
Bilateral Otoplasty
Many patients undergo bilateral otoplasty. This means both ears are operated on for symmetry. Symmetrical ears look more balanced and natural.
Recovery Time
Recovery from otoplasty takes about one to two weeks. Children need rest and should avoid strenuous activities. They usually wear an earband to protect the ears during healing.
Emotional Impact
Children who undergo otoplasty, an ear surgery for abnormal ear shape, often experience a positive change in self-esteem. They feel more confident interacting with peers. This can lead to better social experiences and academic performance at any age, including after ear reshaping or ear surgery.
Preparing for Surgery
Evaluation Process
Doctors use 2D and 3D photos, earband, and plas to plan ear surgery. They also take measurements of the ear projection. This helps create a detailed surgical plan. The plastic surgery team will review these images and measurements, including the ear band. They ensure the best results for the patient.
Pre-Surgery Instructions
Patients must follow strict guidelines before surgery. The doctor will give instructions about eating and drinking. Usually, children cannot eat or drink after midnight before the surgery day. This reduces risks during anesthesia. Parents should make sure their child follows these rules.
Role of Parents
Parents play a crucial role in preparing their child for ear surgery. They should explain the process in simple terms. This helps reduce fear and anxiety. Emotional support is essential for a positive experience.
Anesthesia and Pain Management
The ear surgery usually takes place at an outpatient surgery center. Anesthesia keeps the child asleep during the procedure. After surgery, doctors prescribe pain medicine to manage discomfort. Parents should monitor their child’s pain levels closely.
Post-Surgery Care
After the operation, children need special care. They may wear an ear band to protect their ears. Follow-up appointments are necessary to check healing progress. The doctor will give specific care instructions for home recovery after ear surgery.
The Surgical Process
Pediatric Procedures
Otoplasty for children is a common pediatric plastic surgery. It usually takes place in an outpatient surgical center. This means the child can go home the same day after ear surgery.
The surgeon performs the procedure under general anesthesia. This ensures the child feels no pain during the ear surgery.
Incision Placement
Surgeons make small incisions behind the ears. These incisions are minimally visible once healed. The incision placement is crucial for reducing visible scars.
Dissolvable sutures close the incisions. These sutures do not need removal, making ear recovery easier for children.
Cartilage Alteration
The surgeon reshapes the ear cartilage through these small incisions. Cartilage alteration helps achieve the desired ear shape. Sometimes, excess skin may be removed to improve appearance.
The goal is to create natural-looking ears that are symmetrical with each other.
Bilateral Correction
Otoplasty typically involves bilateral correction. Surgeons adjust both ears to ensure symmetry. This step is important for balanced and natural results.
Symmetry helps boost the child’s confidence and self-esteem.
Post-Surgery Care
After surgery, a bandage covers the ears to protect them. The surgical team provides care instructions to follow at home, including ear care. These include keeping the bandages dry and clean.
Parents should monitor their child’s recovery closely. Any signs of infection or unusual ear pain should be reported to the surgeon immediately.
Potential Surgical Issues
While otoplasty is generally safe, there can be complications. Possible surgical issues include infection, bleeding, or asymmetry. Choosing an experienced surgeon minimizes these risks.
In rare cases, additional corrective surgery may be needed to address any ear problems.
Parental Guidance
Importance of Support
Parents play a crucial role in the otoplasty journey. Children need emotional support before and after surgery. Being there for them can reduce anxiety. Explain the procedure in simple terms.
Explaining the Procedure
Use age-appropriate language when talking to your child. Avoid medical jargon. Say that the doctor will make their ears look better. Reassure them that they will be safe and asleep during the ear surgery.
Pre-Operative Care
Follow all instructions from the pediatrician before the surgery day, especially regarding the ear. Ensure your child is healthy and has no infections. Prepare them mentally by discussing what to expect on the surgery day, keeping an ear out for any concerns.
Post-Operative Care
Adhering to post-operative care is essential for a smooth recovery. Keep your child’s head elevated to minimize swelling. Follow the pediatrician’s advice on ear pain management and activity restrictions.
Post-Surgery Awakening
Child’s Reaction
Children may feel confused upon waking up. The anesthesia can cause disorientation. Some might cry or feel scared. This reaction is normal.
Parents should stay calm. Their presence is comforting. Gentle words and touch help soothe the child.
Recovery Room Care
The recovery room is where immediate post-operative ear care occurs. Nurses monitor vital signs closely. They check heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
Pain management starts here. Medications are given to reduce discomfort. Monitoring pain levels ensures the child remains comfortable.
Parental Reassurance
Parental presence is crucial during this time. Children look for familiar faces when they wake up. Being there reassures them.
Parents can help by:
- Holding their child’s hand
- Speaking softly
- Staying calm and positive
Managing Trauma
Waking up from surgery can be traumatic for some children, especially if they have ear pain. Fear and confusion are common. Parents should understand this and provide support.
Reassuring words and actions reduce trauma effects. Calm demeanor helps the child feel safe.
Time in Recovery Room
The time spent in the recovery room varies. It depends on the child’s response to anesthesia. Most children stay for 1-2 hours.
During this period, nurses ensure the child is stable. Once cleared, they move to a regular room or go home.
Returning Home
Transportation
Ensure the child is comfortable during the ride home. Use a vehicle with ample space. Arrange for someone to sit next to the child. This helps monitor their condition. Bring pillows and blankets for extra comfort.
Settling In
Once home, guide the child to a quiet room. Make sure this area is free from noise and distractions for the ear. Keep the room dimly lit. Provide soft pillows, a cozy blanket, and an ear. Encourage the child to rest as much as possible.
Signs of Complications
Parents need to watch for signs of complications. Look for excessive bleeding around the surgical area. Swelling is normal, but extreme swelling in the ear can be a concern. Check for fever above 100.4°F (38°C). If any of these occur, call the doctor immediately.
Comfort Measures
Create a comfortable environment for recovery. Keep pain medications within easy reach. Follow the doctor’s instructions on dosage and timing. Offer plenty of fluids and light snacks. Avoid foods that require heavy chewing.
Family Support
Family support is crucial during recovery. Ensure someone is always nearby to assist the child. Comforting words and gentle care make a big difference. Engage in quiet activities like reading or watching movies together, ear.
Follow-Up Care
Schedule follow-up appointments as advised by the surgeon. These visits help monitor healing progress. The doctor may remove stitches or adjust bandages during these visits. Keep an eye on the surgical site until fully healed.
Follow-Up Care
Typical Schedule
The follow-up care for otoplasty begins soon after returning home. The first visit usually occurs within a week of surgery. This appointment allows the surgeon to check the initial healing.
Subsequent visits are typically scheduled at:
- Two weeks post-surgery
- One month post-surgery
- Three months post-surgery
These appointments help ensure that the ears are healing properly. Regular check-ups are crucial to monitor the progress and make necessary adjustments.
Importance of Follow-Up
Adhering to follow-up appointments is essential for optimal outcomes. Missing these appointments can lead to unnoticed complications. Nurses play a significant role during these visits. They assist in cleaning wounds and changing dressings.
Parents should take note of any signs of infection or unusual swelling. Reporting these symptoms early can prevent more serious issues. Consistent follow-up ensures that any concerns are addressed promptly.
Potential Adjustments
During the follow-up period, minor revisions might be necessary. These adjustments can include:
- Correcting minor asymmetries
- Addressing any scar tissue formation
- Ensuring proper ear shape retention
In some cases, repeat surgery may be needed. This is rare but possible if initial results are not satisfactory. Surgeons will discuss all options with parents if further procedures are required.
At-Home Recovery Tips
Managing Pain
After otoplasty, children may experience pain. Use prescribed pain medication as directed. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can also help. Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling.
Ear Protection
Keep the ears protected. Use a headband or bandage to secure them in place. This helps avoid accidental bumps or scratches. Ensure the child wears this protection while sleeping.
Maintaining Hygiene
Cleanliness is crucial for healing. Gently clean around the surgical site with mild soap and water. Avoid getting the stitches wet. Pat the area dry with a soft towel.
Limiting Activity
Children should avoid strenuous activities. Running, jumping, and sports can strain healing ears. Encourage quiet activities like reading or drawing. This reduces the risk of injury.
Keeping Engaged
Engage the child in calm activities. Watching movies, playing board games, or doing puzzles can keep them entertained. Limit screen time to prevent eye strain and headaches.
Monitoring Healing
Check the ears daily for signs of infection. Look for redness, swelling, or discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms.
Follow-Up Appointments
Attend all follow-up appointments as scheduled. The doctor will check on the healing process. They may remove stitches during these visits.
Addressing Concerns and Benefits
Common Issues
Parents often worry about the risks of otoplasty. Complications can include infection, scarring, or asymmetry. These are rare but possible. Surgeons take precautions to minimize these risks.
Children with special needs might face additional challenges. It’s essential to discuss these concerns with the surgeon. They can tailor the procedure to meet specific requirements.
Psychological Benefits
Otoplasty can significantly boost a child’s self-esteem. Children with prominent ears might feel self-conscious. This surgery can help them feel more confident.
Improved self-esteem leads to better social interactions. Children may participate more in activities and make friends easily. Feeling accepted by peers is crucial for their emotional well-being.
Social Benefits
Children often face teasing due to physical differences. Otoplasty can reduce this bullying. It helps children fit in better with their peers.
The surgery can also improve a child’s overall happiness. A positive change in appearance can lead to a more optimistic outlook on life. This has long-term benefits for mental health.
Safety and Satisfaction
Otoplasty is generally safe. Most children recover without complications. The procedure has a high satisfaction rate among parents and children alike.
Surgeons use advanced techniques to ensure safety. Post-surgery care is crucial for a smooth recovery. Parents should follow all medical advice closely.
Summary
Otoplasty can be life-changing for your child, offering lasting benefits in confidence and appearance. From preparation to at-home recovery, every step is crucial for a smooth experience and optimal results. By following the guidelines and staying informed, you ensure your child feels supported and comfortable throughout the journey.
Ready to take the next step? Consult with a trusted surgeon today to discuss otoplasty options for your child. Your proactive approach can make all the difference in their well-being and self-esteem. Don’t wait—start now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is otoplasty?
Otoplasty is a surgical procedure to correct the shape, position, or size of the ears. It’s often done to address prominent ears or other ear deformities.
How should we prepare for my child’s otoplasty surgery?
Preparation involves a medical evaluation, discussing anesthesia options, and following pre-surgery guidelines like fasting. Your surgeon will provide specific instructions.
What happens during the otoplasty surgery?
During otoplasty, the surgeon makes incisions behind the ear to reshape cartilage. The procedure usually takes 1-2 hours and is done under general anesthesia.
How can parents support their child through otoplasty?
Parents should offer emotional support, ensure the child understands the process, and follow all pre- and post-operative care instructions from the surgeon.
What should we expect immediately after surgery?
Post-surgery, your child may feel groggy as anesthesia wears off. There might be some swelling and discomfort, which can be managed with prescribed pain medication.
When can my child return home after otoplasty?
Most children can go home the same day after a few hours of observation. Follow your surgeon’s advice on when it’s safe to leave.
What follow-up care is needed after otoplasty?
Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor healing and remove any stitches. Your surgeon will provide a schedule for these visits.
What are some at-home recovery tips for my child?
Ensure your child rests, avoids strenuous activities, and keeps their head elevated. Follow all wound care instructions and keep the surgical site clean and dry.






